Three-physique nuclear programs are key to many aspects of as a lot as the moment nuclear physics, akin to working out the equation of impart of excessive-density nuclear matter and the composition of neutron well-known particular person cores. In relate, scattering data from deuterons (sure proton-neutron pairs) and hadrons provide main substances for constraining parameters of nuclear interactions. Physicists with the ALICE Collaboration display mask that such three-physique nuclear reactions is also investigated by capacity of hadron-deuteron correlations in momentum dwelling at CERN’s Grand Hadron Collider (LHC).
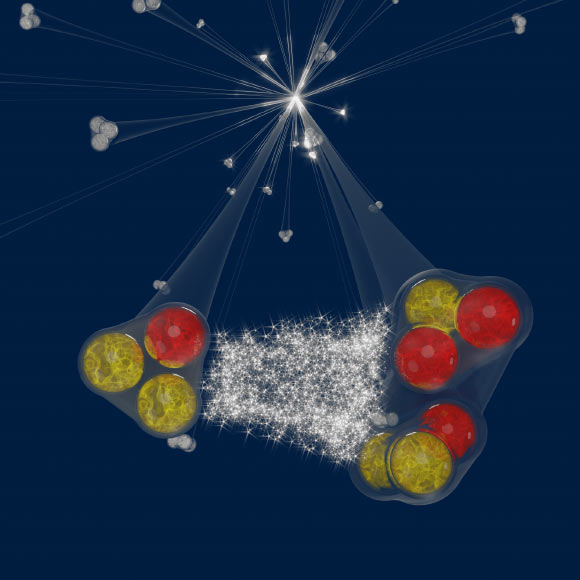
An illustration of the solid interaction within the proton-deuteron plan produced in proton-proton collisions at CERN’s Grand Hadron Collider. Image credit: ALICE / CERN.
A main power is in total described as an interaction between two objects. Extending this to extra complex programs is no longer consistently trivial.
The description of strongly interacting three-hadron programs is key to working out many phenomena in as a lot as the moment nuclear physics, akin to the structure of nuclei, properties of excessive-density nuclear matter and the composition of neutron well-known particular person cores.
Proton-proton collisions on the LHC construct a enormous selection of particles that are emitted very end to 1 but any other, at distances of about 10-15 m (a femtometer).
It’s attention-grabbing to explore whether they impact every other in any manner previous to spraying off in all instructions.
If two particles are produced end to 1 but any other and with the same momenta and route, the pair is also discipline to quantum statistics, Coulomb power and solid interaction.
If belief to be one of many pair is a deuteron, then a tool with a deuteron and one other hadron, fancy a proton or a kaon, is successfully a three-physique plan.
Thus, the measurement of correlations between deuterons and kaons or protons is anticipated to repeat the interactions of three-physique programs.
The ALICE Collaboration utilises its ideally suited particle identification capabilities to explore these correlations in excessive-multiplicity proton-proton collisions at a centre-of-mass vitality of 13 TeV.
The atomize result is a correlation feature that measures how the likelihood of finding two particles with sure relative momenta differs from what could maybe be anticipated if their momenta were fully independent or uncorrelated.
In the absence of correlation, the rate of the feature is solidarity.
A price above one indicates rapid-witted interaction, whereas a price below one indicates shocking interaction.
The correlation functions for each the kaon-deuteron and proton-deuteron programs are below solidarity for low relative transverse momenta, indicating an total shocking interaction.
The diagnosis of the kaon-deuteron correlation shows that the relative distances at which deuterons and protons or kaons are produced are relatively tiny, around 2 fm.
The kaon-deuteron correlations are successfully described with an efficient two-physique model that accommodates each the Coulomb interaction and solid interaction between the kaon and the deuteron.
In distinction, the identical efficient two-physique capacity fails to describe the proton-deuteron correlations, necessitating a paunchy three-physique calculation that accounts for the structure of the deuteron.
An ideally suited data description is finished the exercise of theoretical calculations that tale for each two- and three-physique solid interactions.
This demonstrates the sensitivity of the correlation feature to the rapid-vary dynamics of the three-nucleon plan.
The correlation measurements at rapid distances picture an innovative methodology to explore three-physique programs on the LHC, with the aptitude to elongate such reviews to other hadrons.
“Our result establishes a new experimental methodology to explore the dynamics and forces of three-physique nuclear programs with precision,” the physicists acknowledged.
“Certainly, given the copious manufacturing of bizarre and enchantment particles on the nuclear collisions on the LHC, the supplied methodology sets the stage for the explore of three-physique forces in programs with strangeness and enchantment in a advise manner.”
Their paper became once published within the journal Bodily Review X.
_____
S. Acharya et al. (ALICE Collaboration). 2024. Exploring the Tough Interaction of Three-Physique Programs on the LHC. Phys. Rev. X 14 (3): 031051; doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.14.031051