Utilizing genome, transcriptome, and proteome analysis of the newly-stumbled on species of tardigrade, named Hypsibius henanensis, scientists explored the molecular basis contributing to radiotolerance in these tiny invertebrates.
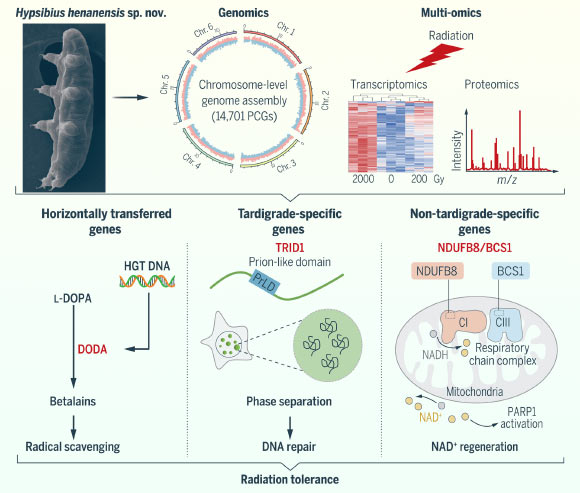
Schematic of mechanisms that confer radiotolerance to Hypsibius henanensis. Characterize credit: Li et al., doi: 10.1126/science.adl0799.
Tardigrades, also acknowledged as water bears or moss piglets, are a diverse community of little invertebrates properly-known for their potential to stand as a lot as indecent prerequisites.
First show screen in 1773, these creatures can dwell for as a lot as 60 years, and grow to a most measurement of 0.5 mm, easiest viewed below a microscope.
They’re in a position to outlive for as a lot as 30 years with out food or water, for a quick time at temperatures as minute as minus 272 levels Celsius (minus 457 levels Fahrenheit) or as high as 150 levels Celsius (302 levels Fahrenheit), and minus 20 levels Celsius (minus 4 levels Fahrenheit) for a long time.
They stand as a lot as pressures from with regards to 0 atm in attach aside as a lot as 1,200 atm on the bottom of the Marianas Trench.
In addition they demonstrate outstanding resistance to ionizing radiation, withstanding doses as high as 3,000 to 5,000 grays (Gy) of gamma rays, which is roughly 1,000 times the lethal dose for other folks.
The mechanism of radiotolerance in tardigrades remains largely unclear.
Old experiences investigating how they stop this possess confirmed that tardigrades dangle strong DNA restore capabilities.
In addition they yelp a tardigrade-explicit protein called afflict suppressor (Dsup), which, when expressed in human cells, protects DNA from radiation afflict.
In fresh analysis, Qingdao College Lei Li and colleagues described a brand fresh species of tardigrade: Hypsibius henanensis.
Through detailed morphological and molecular analysis, besides they explored the premise of the species’ radiotolerance.
The researchers evaluated how publicity to heavy ion radiation altered the animal’s molecular profiles. They stumbled on that 285 stress-connected genes were upregulated.
They further uncovered three molecular mechanisms that make a contribution to radiotolerance in the organisms.
First, the horizontally transferred bacterial gene DOPA dioxygenase 1 (DODA1) enhanced radiation resistance by producing betalains — pigments with potent free radical scavenging properties in total show screen in vegetation, fungi, and bacteria.
Second, a tardigrade-explicit protein, TDP1, facilitates the restore of DNA double-strand breaks.
Lastly, the mitochondrial chaperone gene BCS1, which expanded at some stage in tardigrade evolution, is uniquely upregulated based on radiation, shielding cells from radiation-induced mitochondrial afflict.
“Ugly environmental resistance of extremophiles corresponding to tardigrades is a like trove of unexplored molecular mechanisms of stress resistance,” the authors mentioned.
“Purposeful analysis on these radiotolerance mechanisms will further develop our working out of mobile survival below indecent prerequisites and could perhaps merely present inspiration for selling human properly being and combating disease.”
The outcomes were published October 25, 2024 in the journal Science.
_____
Lei Li et al. 2024. Multi-omics panorama and molecular basis of radiation tolerance in a tardigrade. Science 386 (6720); doi: 10.1126/science.adl0799