In 1961, American astrophysicist and astrobiologist Dr. Frank Drake devised an equation wherein a lot of components are multiplied together to estimate the replacement of intellectual civilizations in our Milky Contrivance Galaxy able to making their presence known to humans. More than 60 years on, astrophysicists beget produced a varied mannequin which as a replace specializes in the stipulations created by the acceleration of the Universe’s expansion and the amount of stars shaped. It is conception this expansion is being driven by darkish energy that makes up extra than two thirds of the Universe.

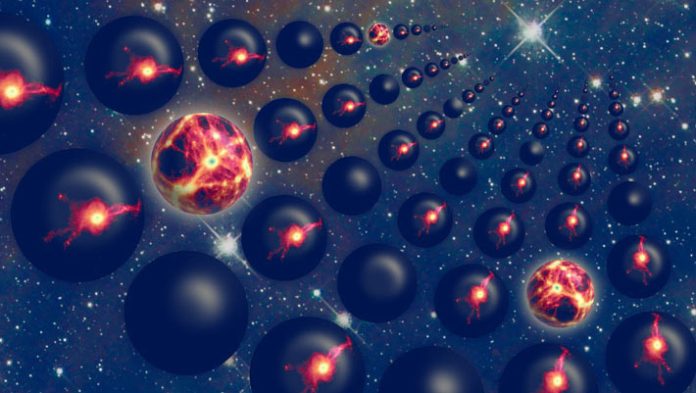
Inventive affect of a Multiverse. Image credit ranking: Jaime Salcido / EAGLE Collaboration.
“Notion darkish energy and the affect on our Universe is one of the important greatest challenges in cosmology and primary physics,” acknowledged Dr. Daniele Sorini, a researcher at Durham University’s Institute for Computational Cosmology.
“The parameters that govern our Universe, together with the density of darkish energy, could most doubtless also indicate our beget existence.”
Since stars are a precondition for the emergence of life as we’re unsleeping of it, the team’s unique mannequin could most doubtless also be feeble to estimate the likelihood of manufacturing intellectual life in our Universe, and in a multiverse scenario of hypothetical varied universes.
The unique research would not strive to calculate the absolute replacement of observers (i.e. intellectual life) in the Universe however as a replace considers the relative likelihood of a randomly chosen observer inhabiting a universe with particular properties.
It concludes that a identical previous observer would query to experience a substantially better density of darkish energy than is considered in our beget Universe — suggesting the ingredients it possesses compose it a rare and extraordinary case in the multiverse.
The methodology presented in the paper entails calculating the allotment of frequent topic converted into stars over the total history of the Universe, for quite quite quite a bit of darkish energy densities.
The mannequin predicts this allotment would be approximately 27% in a universe that’s most atmosphere pleasant at forming stars, compared with 23% in our beget Universe.
This implies we don’t are living in the hypothetical Universe with the very ultimate odds of forming intellectual life kinds.
Or in varied words, the worth of darkish energy density we check up on in our Universe is just not the individual that will maximise the probabilities of life, consistent with the mannequin.
“Surprisingly, we came across that even a seriously increased darkish energy density would aloof be like minded with life, suggesting we’d also not are living in the most doubtless of universes,” Dr. Sorini acknowledged.
The mannequin could most doubtless also enable scientists to mark the outcomes of differing densities of darkish energy on the formation of structures in the Universe and the stipulations for all times to present in the cosmos.
Sad energy makes the Universe expand sooner, balancing gravity’s pull and developing a universe where each and each expansion and construction formation are conceivable.
Nonetheless, for all times to present, there would beget to be regions where topic can clump together to bear stars and planets, and it could perchance per chance most doubtless need to remain stable for billions of years to enable life to adapt.
Crucially, the research means that the astrophysics of neatly-known person formation and the evolution of the substantial-scale construction of the Universe mix in a refined methodology to search out out the optimal rate of the darkish energy density important for the generation of intellectual life.
“It’d be racy to make employ of the mannequin to stumble on the emergence of life across varied universes and look for whether some primary questions we inquire ourselves about our beget Universe need to aloof be reinterpreted,” acknowledged Université de Genève’s Professor Lucas Lombriser.
The look for used to be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Mammoth Society.
_____
Daniele Sorini et al. 2024. The affect of the cosmological constant on previous and future neatly-known person formation. MNRAS 535 (2): 1449-1474; doi: 10.1093/mnras/stae2236