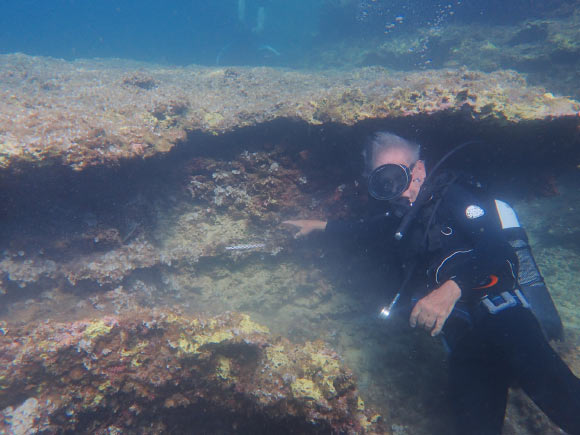
The island of Sicily is regarded as to be amongst the first occupied by folk within the European Upper Paleolithic. Study to like early occupation of the island are mostly focused on the northern shores. A world team of archaeologists led by Washington University in St. Louis has now sought for the human occupation traces in 25 caves and rock shelters in southeastern Sicily, Italy.
Coastal and underwater cave sites in southern Sicily possess crucial fresh clues about the direction and destiny of early human migrants to the island. Image credit: Ilaria Patania.
Sicily, the largest Mediterranean island, is regarded as by many scholars to be the earliest island within the place to be permanently occupied by human ancestors, however when and the strategy the early migrants executed this feat stays unknown.
This island is decrease than two miles from mainland Italy, however the water crossing would bask in been extraordinarily entertaining for early folk.
In the feeble Greek poem the Odyssey, Homer describes how Odysseus sailed his ship previous the legendary sea monsters Scylla and Charybdis as he crossed the Sicily strait.
The strait used to be neatly-known to sailors of the previous; they attributed the lethal forces of its waves and whirlpools to extremely efficient monsters.
In up to date times, thousands of migrants from North Africa try to irascible the strait every Three hundred and sixty five days. Many don’t sort it, some capsizing wonderful a few hundred meters from touchdown.
“What we’re looking for is no longer wonderful the first particular person that arrived, however the first neighborhood,” talked about Dr. Ilaria Patania, a researcher at Washington University in St. Louis.
“Working out the timing of the initial colonization of Sicily affords key files for the pattern and mode of the early expansion of Homo sapiens into the Mediterranean.”
“This review reveals that fresh ways of thinking and looking can demonstrate patterns that weren’t visible earlier than,” added Washington University in St. Louis Professor T.R. Kidder.
“Outdated scholars assumed that sites on the southern float of Sicily might perchance perchance be eroded or too broken to yield in actual fact helpful files.”
“But discovering underwater sites opens up a full fresh terrain to survey.”
“It permits us to re-evaluate routes of migration of these earliest up to date human ancestors.”
Scholars agree that folk had made it to Sicily by 16,000 years after the Final Glacial Most.
But that established date is puzzlingly unhurried, on condition that folk are known to bask in dispersed by land into Siberia about 30,000 years earlier.
The discrepancy has led some to wonder if folk in actuality arrived on Sicily unprecedented earlier than the currently accredited dates.
Moreover, no person but knows whether or no longer folk arrived on Sicily by seafaring, or by foot over a land bridge — and even what route they came from.
“A disaster for determining the spread of early up to date human ancestors is that we don’t fully know how they spread and colonized the enviornment at a in actuality early stage,” Professor Kidder talked about.
“Did other folks strategy down from Italy and irascible the Straits of Messina, or did they strategy from the south alongside the African float?”
“Or, is it doubtless that they bask in been island hopping across the Mediterranean? Locating sites on the south float helps us rob into consideration pathways and thus modes of behavior.”
“In southeast Sicily, completely a few Upper Paleolithic sites bask in been excavated and analyzed using scientific strategies,” Dr. Patania talked about.
“Our mission is restful in its early stages, however already now we bask in identified and assessed over 40 sites of ardour, of which about 17 are sites that bask in been relocated with higher precision primarily primarily primarily based on older identifications.”
Two of the fresh sites identified by the team might perchance just possess Upper Paleolithic human occupation traces, alongside side fossil fauna.
Corruggi is positioned on the southernmost tip of Sicily. The repute used to be on the origin identified by other researchers within the 1940s.
“This web web page online online is where a 2d land bridge would bask in connected this island with the island of Malta,” Dr. Patania talked about.
“When we inspected this web web page online online, we found enamel from a European wild ass and stone tools.”
“Examining the stays from this web web page online online might perchance give us insight on the very closing leg of the human bolt south into the southernmost float of Sicily and off against Malta.”
All the strategy thru summer 2024, the archaeologists labored on excavating the 2d web web page online online, a cave known as Campolato.
“Here now we bask in found evidence for sea-stage changes triggered by the closing glaciation and a localized earthquake that we’re restful investigating,” Dr. Patania talked about.
“We hope to reconstruct no longer finest the timing of human occupation, however also the atmosphere these folk lived in and the strategy they negotiated with natural events like earthquakes, climatic and environmental changes and even most definitely volcanic eruptions.”
The findings appear within the journal PLoS ONE.
_____
I. Patania et al. 2024. Between land and sea: A multidisciplinary system to just like the Early Occupation of Sicily (EOS). PLoS ONE 19 (10): e0299118; doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299118
This article is a model of a press-release supplied by Washington University in St. Louis.