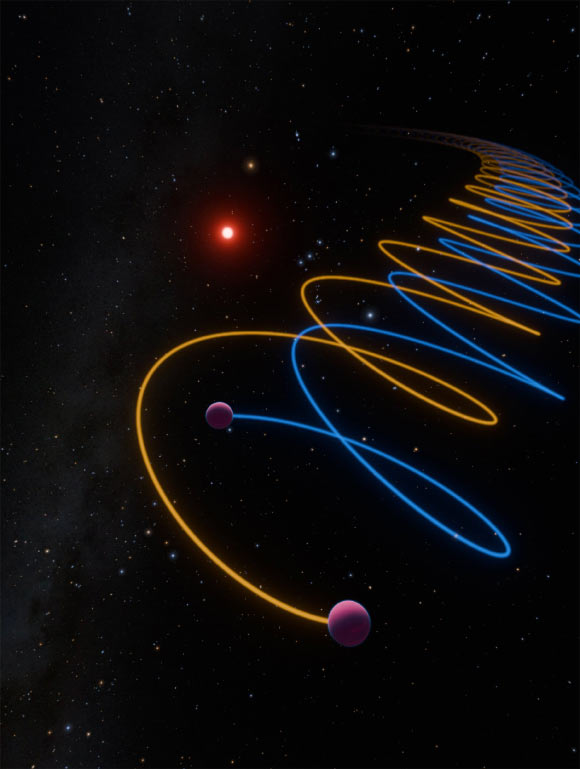
Gliese 229B turned into once the first identified brown dwarf, chanced on in 1995. In new analysis, astronomers noticed Gliese 229 B with the GRAVITY interferometer and, one at a time, the CRIRES+ spectrograph at ESO’s Very Astronomical Telescope. Each units of observations independently resolved Gliese 229B into two parts, Gliese 229 Ba and Bb. They orbit every diversified every 12.1 days with a semimajor axis of 0.042 monumental units (AU) and have heaps of 38.1 and 34.4 Jupiter plenty, respectively.
This artwork highlights a pair of brown dwarfs, named Gliese 229 Ba and Gliese 229 Bb. Image credit score: Good sufficient. Miller / R. Effort / Caltech / IPAC.
Gliese 229B turned into once first chanced on in 1995 but it turned into once too shadowy for its mass.
Whereas astronomers had measured its mass to be about 70 Jupiter plenty, a brown dwarf of that heft must shine extra brightly than what telescopes had noticed.
“Scientists suspected Gliese 229B may perchance well furthermore very smartly be twins, but to evade search for by astronomers for 30 years, the two brown dwarfs would must be very shut to every diversified,” said Caltech graduate pupil Jerry Xuan.
“Seeing the first object smaller than a large name orbiting one other solar turned into once exhilarating,” said Dr. Rebecca Oppenheimer, an astrophysicist on the American Museum of Natural History.
“It started a cottage industry of of us searching out oddballs treasure it back then, but it remained an enigma for a protracted time.”
In the brand new analysis, the astronomers chanced on that Gliese 229B is genuinely a pair of tight-knit brown dwarfs, weighing about 38 and 34 instances the mass of Jupiter, that whip around every diversified every 12 days.
The noticed brightness stages of the pair match what’s expected for two tiny, shadowy brown dwarfs on this mass vary.
“This discovery that Gliese 229B is binary not handiest resolves the unique tension noticed between its mass and luminosity but furthermore tremendously deepens our working out of brown dwarfs, which straddle the line between stars and enormous planets,” said Professor Dimitri Mawet, an astronomer at Caltech and NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
To procure to the bottom of Gliese 229B into two objects, the astronomers ragged two diversified devices, both based at ESO’s Very Astronomical Telescope.
They ragged the GRAVITY instrument, an interferometer that combines light from four diversified telescopes, to spatially procure to the bottom of the physique into two, and they ragged the CRIRES+ instrument to detect determined spectral signatures from the two objects.
The observations showed that the brown dwarf duo, now known as Gliese 229Ba and Gliese 229Bb, orbit every diversified every 12.1 days with a separation handiest 16 instances better than the distance between Earth and the Moon.
Together, the pair orbit the M-dwarf large name Gliese 229A once every 250 years.
“These two worlds whipping around every diversified are genuinely smaller in radius than Jupiter,” Dr. Oppenheimer said.
“They’d survey slightly unparalleled in our evening sky if we had one thing treasure them in our bask in Solar System.”
“Here is principally the most fun and engaging discovery in substellar astrophysics in decades.”
The invention is reported in a paper in the journal Nature.
_____
J.W. Xuan et al. The frigid brown dwarf Gliese 229B is a shut binary. Nature, printed online October 16, 2024; doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08064-x