Astronomers the utilization of the NASA/ESA Hubble Home Telescope private captured a glossy new image of the unbarred spiral galaxy NGC 4414.
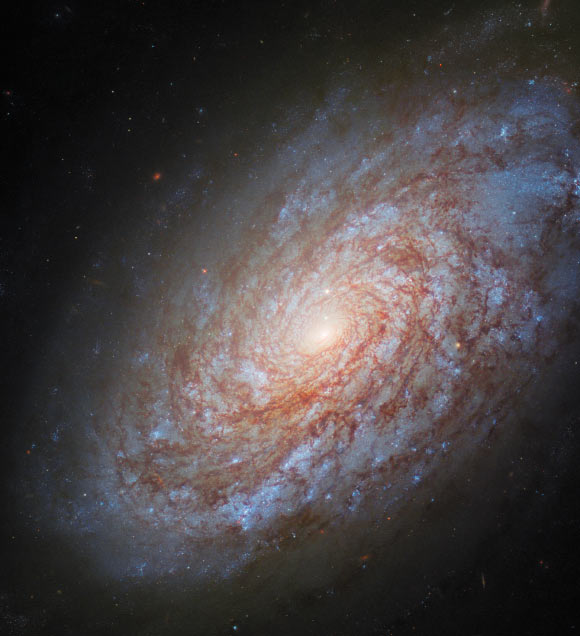
This Hubble image shows NGC 4414, an unbarred spiral galaxy located 51 million mild-years away within the constellation of Coma Berenices. List credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / O. Graur / S.W. Jha / A. Filippenko.
NGC 4414 resides roughly 51 million mild-years some distance flung from Earth within the constellation of Coma Berenices.
Additionally identified as the Dusty Spiral Galaxy, Ark 365, IRAS 12239+3129, LEDA 40692 or UGC 7539, this galaxy has a diameter of about 56,000 mild-years.
NGC 4414 change into once first learned on March 13, 1785 by the German-born British astronomer William Herschel.
The galaxy belongs to the Coma I Neighborhood, a team of galaxies end to the Virgo Cluster.
NGC 4414 change into once beforehand seen by Hubble in 1995 and in 1999 as half of a study effort to thought Cepheid variable stars.
This collage facets supernovae seen by Hubble in NGC 4414. After all left is a neat spiral galaxy is viewed tilted diagonally. Every subsequent panel shows a end-up of the galaxy in 1999, 2021, and 2023 to specialise within the galaxy’s supernovae. List credit: NASA / ESA / Hubble / O. Graur / S.W. Jha / A. Filippenko.
“Cepheids are a special form of variable massive title with very trusty and predictable brightness adaptations,” Hubble astronomers said in an announcement.
“The interval of these adaptations is reckoning on bodily properties of the celebrities equivalent to their mass and merely brightness.”
“This implies that astronomers, appropriate by taking a thought at the vary of their mild, can uncover about the Cepheids’ bodily nature, which then would per chance perhaps also very neatly be susceptible very effectively to search out out their distance.”
“This is why cosmologists call Cepheids ‘usual candles’.”
“Astronomers private susceptible Hubble to study Cepheids, fancy these that stay in NGC 4414, with extraordinary results.”
“The Cepheids private then been susceptible as stepping-stones to make distance measurements for supernovae, which private, in flip, given a measure for the size of the Universe.”
“On the present time we know the age of the Universe to an out of this world elevated precision than before Hubble: around 13.7 billion years.”