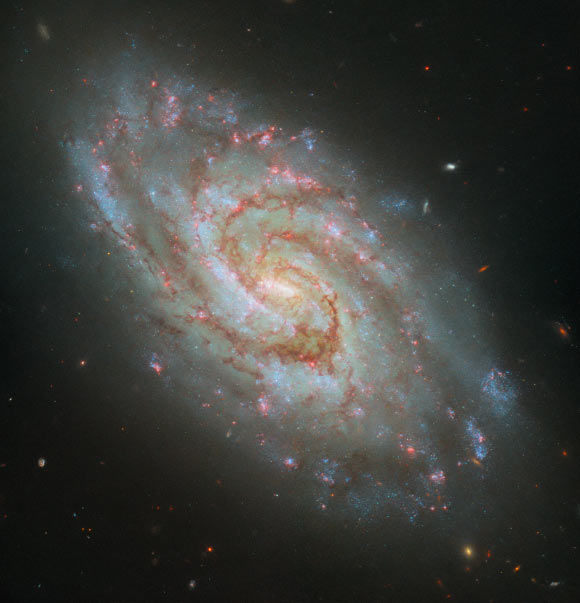
The Hubble team of workers has released a unparalleled unique whisper snapped by the NASA/ESA Hubble Field Telescope of the barred spiral galaxy IC 1954.
This Hubble whisper reveals IC 1954, a tiny barred spiral galaxy situated Forty five million light-years away in the constellation of Horologium. Characterize credit ranking: NASA / ESA / Hubble / D. Thilker / J. Lee / PHANGS-HST Personnel.
IC 1954 lies some Forty five million light-years away from Earth in the southern constellation of Horologium.
This tiny spiral galaxy was realized in 1898 by the Scottish astronomer Robert Innes.
Otherwise identified as ESO 200-36, IRAS 03300-5204 or LEDA 13090, it has a diameter of 20,000 light-years.
IC 1954 has a shimmering central bar and lazily winding spiral arms threaded with darkish clouds of dirt.
Along with four other galaxies, it forms the LGG 93 galaxy team, additionally called the IC 1954 team.
“IC 1954 sports actions a elegant bar in its core, two fundamental majestically winding spiral arms and clouds of darkish dirt across it,” the Hubble astronomers acknowledged in a assertion.
An whisper of IC 1954 was previously released by the Hubble team of workers in 2021. The unique whisper now involves H-alpha data.
“The improved coverage of large name-forming nebulae, which will likely be worthy emitters of the red H-alpha light, can also additionally be considered in the different elegant, purple spots across the disk of the galaxy,” the researchers acknowledged.
“Apparently, some astronomers posit that the galaxy’s ‘bar’ is in actuality an brisk huge name-forming location that actual form occurs to lie over the galactic center.”
The coloration whisper of IC 1954 was product of separate exposures taken in the considered, ultraviolet and stop to-infrared regions of the spectrum with Hubble’s Huge Field Camera 3 (WFC3).
Six filters were common to sample assorted wavelengths. The coloration outcomes from assigning diversified hues to each and every monochromatic whisper associated with a individual filter.
“By surveying IC 1954 and over fifty other nearby galaxies in radio, infrared, optical, and ultraviolet light, astronomers aim to fully imprint and reconstruct the disappear matter takes through stars and the interstellar fuel and dirt in each and every galaxy,” the scientists acknowledged.
“Hubble’s looking out at capabilities maintain a wanted fragment of this scrutinize: it’ll grab youthful stars and big name clusters as soon as they’re brightest at ultraviolet and optical wavelengths, and its H-alpha filter effectively tracks emission from nebulae.”
“The ensuing dataset will maintain a admire trove of research on the evolution of stars in galaxies, which the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Field Telescope will produce upon as it continues its science operations into the future.”