Polar vortices are present in planetary atmospheres, from the Earth-adore rocky planets to Jupiter- and Saturn-adore gas giants. Nonetheless, no longer significant is known about their existence and characteristics on our Sun attributable to the present lack of hiss observations on the poles. Unlike planetary atmospheres, the subsurface layers of the Sun are highly influenced by the presence of magnetic fields. Contemporary learn reveals that solar cycle magnetic fields present a mechanism for the formation of polar vortices in the Sun.

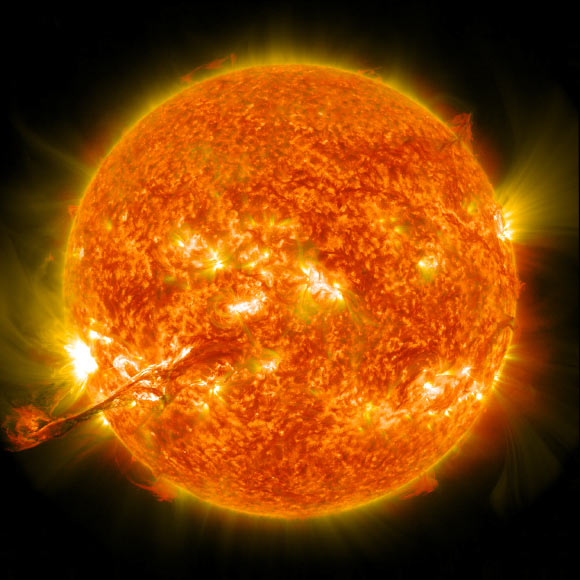
On August 31, 2012, a protracted filament of solar fabric that had been hovering in the Sun’s atmosphere, the corona, erupted out into house at 4:36 p.m. EDT. The CME traveled at over 900 miles per second. It didn’t journey back and forth at once toward Earth, but did join with Earth’s magnetic atmosphere, or magnetosphere, with a glancing blow, inflicting aurora to appear on the evening of September 3. Image credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
“Nobody can explain for certain what’s going down on the solar poles,” said Dr. Mausumi Dikpati, a senior scientist with the Excessive Altitude Observatory at NSF-Nationwide Center for Atmospheric Study.
“But this novel learn provides us an intriguing gaze at what we would interrogate to procure when we’re ready, for the first time, to ogle the solar poles.”
The doubtless presence of some form of polar vortices on the Sun would no longer strategy as a surprise.
These spinning formations manufacture in fluids that surround a rotating physique attributable to the Coriolis force, and they’ve been observed on the broad majority of planets in our Characterize voltaic Design.
On Earth, a vortex spins excessive in the atmosphere around each and every the north and south poles.
When those vortices are proper, they support frigid air locked on the poles, but when they weaken and change into unstable, they permit that chilly air to seep toward the equator, inflicting chilly air outbreaks in the midlatitudes.
NASA’s Juno mission returned breathtaking pictures of polar vortices on Jupiter, exhibiting eight tightly packed swirls all the device in which by the gas monumental’s north pole and 5 around its south.
The polar vortices on Saturn, viewed by NASA’s Cassini spacecraft, are hexagonally shaped in the north pole and extra circular in the south.
These differences offer scientists clues into the make-up and dynamics of every and every planet’s atmosphere.
Polar vortices beget also been observed in Mars, Venus, Uranus, Neptune, and Saturn’s moon Titan, so in many ways, the fact that the Sun (also a rotating physique surrounded by a fluid) would beget such substances would be evident.
However the Sun would possibly perchance be basically a amount of from the planets and moons that comprise atmospheres: the plasma that surrounds the Sun is magnetic.
How that magnetism would possibly perchance well affect the formation and evolution of solar polar vortices — or whether or no longer they devise in any respect — is a thriller on story of humanity has by no device despatched a mission into house that can ogle the Sun’s poles.
Truly our observations of the Sun are slight to views of the face of the Sun because it capabilities toward Earth and most attention-grabbing provides hints at what’s liable to be transpiring on the poles.
Since astronomers beget by no device observed the Sun’s poles, the behold authors relied on computer gadgets to non-public in the blanks about what solar polar vortices would possibly perchance well gaze adore.
What they stumbled on is that the Sun is liable to indeed beget a outlandish pattern of polar vortices that evolves as the solar cycle unfolds and is decided by the strength of any explicit cycle.
In the simulations, a correct ring of polar vortices forms at around 55 levels latitude — the same of Earth’s Arctic circle — on the identical time that a phenomenon known as the ‘hunch to the poles’ begins.
At essentially the most of every and every solar cycle, the magnetic area on the Sun’s poles disappears and is changed with a magnetic area of reverse polarity.
This flip-flop is preceded by a ‘hunch to the poles’ when the area of reverse polarity begins to journey back and forth from about 55 levels in latitude poleward.
After forming, the vortices head toward the poles in a tightening ring, shedding vortices as the circle closes, eventually leaving most attention-grabbing a pair of vortices at once abutting the poles earlier than they fade altogether at solar most.
What number of vortices invent and their configuration as they circulate toward the poles adjustments with the strength of the solar cycle.
These simulations offer a missing fragment to the puzzle of how the Sun’s magnetic area behaves almost about the poles and can lend a hand acknowledge some elementary questions about the Sun’s solar cycles.
As an illustration, previously many scientists beget outdated-authentic the strength of the magnetic area that ‘rushes to the poles’ as a proxy for the style proper the upcoming solar cycle is liable to be.
However the mechanism for the style those things would possibly perchance well join, if in any respect, is no longer obvious.
The simulations also offer recordsdata that would be outdated-authentic for planning future missions to ogle the Sun.
Particularly, the outcomes level to that some invent of polar vortices must always be observable all the device in which by all substances of the solar cycle besides all the device in which by the solar most.
“Possibilities are you’ll presumably furthermore commence a solar mission, and it’d furthermore components to ogle the poles at fully the antagonistic time,” said Dr. Scott McIntosh, also from the Excessive Altitude Observatory at NSF-Nationwide Center for Atmospheric Study.
The Characterize voltaic Orbiter, a cooperative mission between NASA and ESA, would possibly perchance well furthermore give researchers their first glimpse of the solar poles, however the first gaze will be almost about solar most.
The scientists expose that a mission designed to ogle the poles and to give researchers a pair of, simultaneous viewpoints of the Sun would possibly perchance well furthermore lend a hand them acknowledge many long-held questions about the Sun’s magnetic fields.
“Our conceptual boundary now would possibly perchance presumably be that we’re working with most attention-grabbing one level of view,” Dr. McIntosh said.
“To originate foremost growth, we’re going to must always beget the observations we desire to ascertain our hypotheses and make distinct whether or no longer simulations adore these are engaging.”
The outcomes appear in the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
_____
Mausumi Dikpati et al. 2024. A magnetohydrodynamic mechanism for the formation of solar polar vortices. PNAS 121 (47): e2415157121; doi: 10.1073/pnas.2415157121